양자가설에 관해-백과사전에서
토마스 영의 이중 슬릿실험 이후로 과학자들은 빛을 파동으로 생각했고
James Clerk Maxwell은 빛은 전자와 자기로 되어있고 전자파와 자기파가 함께 움직인다고 주장했다.
당시 흑체복사의 스펙트럼 (ultraviolet catastrophe), 광전효과, 러더퍼드의 원자모형은 당시 설명하기 힘든 현상이었다.
막스 플랑크는 빛은 에너지의 패킷(packets)의 연속이라는 양자가설을 고안했고
아인슈타인은 빛이 입자로 되어있어 물질과 서로 작용한다며 광전효과를 통해 증명했다. .
이처럼 빛이 입자로 되어있고 파로 움직인다는 것을 막스 플랑크와 아인슈타인에 의해 발견되었다.
닐스보어는 러더퍼드의 원자모형에 양자개념을 도입하여 원자 모형을 만들었고 이것이 양자역학이 시작이 되었다.

독일의 물리학자 막스 플랑크 (Max Planck; 1858 ~ 1947)
현대물리학에 중요한 수많은 업적을 이루었다.
막스 플랑크 - 양자가설
1890년대 The German Bureau of Standard에서 막스 플랑크에게 효율적인 전구 제작방법을 요청했다. 막스 플랭크는 전구안에 든 필라멘트가 얼마나 많은 빛을 방출하는지 예측하고자 했다. 흑체복사 실험 결과 고전 물리학 이론과 맞지않자 1900년 그는 흑체복사 스펙트럼에 대한 수학적인 예측방법에 양자가설을 고안했다. 즉 빛과 같은 전자기에너지 (electromagnetic energy)가 물처럼 고르게 흘러들어오는 대신 모래알처럼 패킷(packets)의 연속으로 들어온다고 가정했다. 그는 이 패킷을 양자(quantum)라 불렀다. 그것을 그의 공식에 적용하니 놀랍게도 잘 맞았다.
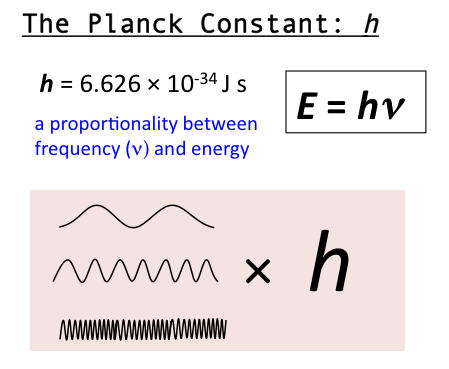
- 에너지의 세기 = 플랑크 상수 * 진동수 (E = hv); 즉 빛의 에너지는 연속적인 물리량이 아니다.
- 에너지는 온도와 관계없고 색깔 즉 진동수 (frequency)와 관계가 있다. 빨간색의 파장은 650 nm (나노미터)정도이고 파란색은 500 nm정도이다. 진동수는 1초동안 만들어지는 파장수이므로 파란색이 빨간색보다 진동수가 크다. 즉 파란색빛이 빨간색 빛 보다 에너지세기가 크므로 더 뜨겁다.
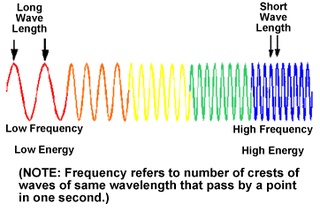
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i1TVZIBj7UA

아인슈타인 - 광전효과 (photoelectric effect)로 양자 (quantum)를 증명함
플랑크는 수학적 편의로 양자가설을 생각해냈지만 5년후 아인슈타인은 광전효과를 증명하면서 플랑크의 광양자를 실제 물리적 존재라는 것을 알아냈다. 광전효과란 빛이 금속물에 쏘이면 금속물은 전자를 방출한다는 것이다. 즉 전류의 흐름이 발생한다. 금속물질들은 서로 다른 한계 주파수 (threshold frequency)를 가지고 있어 일정한 주파수 이상이여야 전자가 튀어나온다.

닐스보어 - 원자모형에 양자개념을 도입하면서 양자역학의 시작이 됨
닐스보어는 러더퍼드의 원자 모형을 수정하여 원자 모형에 막스플랑크의 양자 개념을 도입 양자화된 궤도를 설정하였다. 전자는 바닥상태에서 에너지를 흡수하여 더 높은 에너지 를 가진 궤도로 가 들뜬 상태로 되기도 하고 반대로 흡수했던 에너지를 방출하고 원래있던 궤도로 갈 수 도 있다. 이것을 quantum leap (jump)라고 한다. 이것으로 에너지는 연속적인 물리량이 아니라는 것을 증명했고 또한 수소원자가 내는 스펙트럼의 진동수를 설명하는데 성공했다. 이것이 양자역학 (quantum mechanics)라 불리는 새로운 물리분야의 시작이었다.
Looking into Atoms
Quantum physics is a branch of physics that works with the activities going on inside of atoms. They talk about subatomic particles interacting with each other. We're starting to talk about Albert Einstein and Max Planck'sideas here. In the early 1900's, scientists were beginning to examine the inside of atoms. They were wondering what was going on inside those things that were once thought to be solid. one big idea they came up with was that the energy of an electron depends on the frequency, or wavelength, of theEM Radiation. Another interesting idea they discovered was that energy didn't depend on the intensity, or amount, of radiation.
If you apply this idea to the structure of an atom, in the older, Bohr model, there is a nucleus and there are rings (levels) of energy around the nucleus. The length of each orbit was related to a wavelength. No two electrons can have all the same wave characteristics. Scientists now say that electrons behave like waves, and fill areas of the atom like sound waves might fill a room. The electrons, then, exist in something scientists call "electron clouds". The size of the shells now relates to the size of the cloud. This is where the spdf stuff comes in, as these describe the shape of the clouds.
Packets of Energy
During the early 1900's scientists also discovered that EM radiation not only moves like a wave, but has packs of energy (quanta) as well. It's like a stream of individual packets.
